Java初级测试题七-面向对象高级特性(6-6)
Java初级测试题七-面向对象高级特性(6-6)
注意
本博文仅供学术研究和交流参考,严禁将其用于商业用途。如因违规使用产生的任何法律问题,使用者需自行负责。
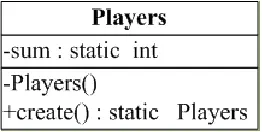
- 创建一个球员类,并且该类最多只允许创建十一个对象。提示利用 static 和 封装性来完成。
类图如下:
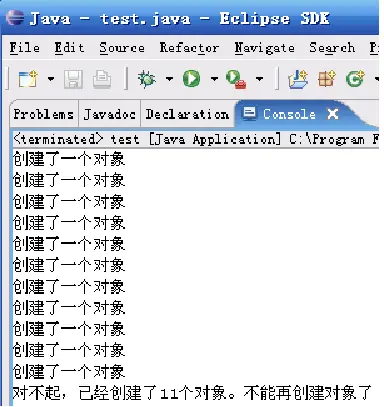
效果如下:
package chapter7;
public class Players {
// 1、创建一个球员类,并且该类最多只允许创建十一个对象。
// 提示利用 static 和 封装性来完成。
private static int sum;
/**
* 无参构造方法
*/
private Players()
{
}
public static Players create()
{
sum = 1;
Players players = null;
while(sum <= 11)
{
players = new Players();
System.out.println("创建咯"+sum+"个对象");
sum++;
}
System.out.println("对不起,已经创建咯11个对象,不能再创建对象了");
return players;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Players.create();
}
}
- 设计2个类,要求如下:(知识点:类的继承 方法的覆盖)
2.1 定义一个汽车类Vehicle,
2.1.1 属性包括:汽车品牌brand(String类型)、颜色color(String类型)和速度speed(double类型)。
2.1.2 至少提供一个有参的构造方法(要求品牌和颜色可以初始化为任意值,但速度的初始值必须为0)。
2.1.3 为属性提供访问器方法。注意:汽车品牌一旦初始化之后不能修改。
2.1.4 定义一个一般方法run(),用打印语句描述汽车奔跑的功能
2.1.5 在main方法中创建一个品牌为“benz”、颜色为“black”的汽车。
2.2 定义一个Vehicle类的子类轿车类Car,要求如下:
2.2.1 轿车有自己的属性载人数loader(int 类型)。
2.2.2 提供该类初始化属性的构造方法。
2.2.3 重新定义run(),用打印语句描述轿车奔跑的功能。
2.2.4 在main方法中创建一个品牌为“Honda”、颜色为“red”,载人数为2人的轿车。
package chapter7;
public class Vehicle {
// 2、设计2个类,要求如下:(知识点:类的继承 方法的覆盖) [必做题]
// 2.1 定义一个汽车类Vehicle,
// 2.1.1 属性包括:汽车品牌brand(String类型)、颜色color(String类型)和速度speed(double类型)。
// 2.1.2 至少提供一个有参的构造方法(要求品牌和颜色可以初始化为任意值,但速度的初始值必须为0)。
// 2.1.3 为属性提供访问器方法。注意:汽车品牌一旦初始化之后不能修改。
// 2.1.4 定义一个一般方法run(),用打印语句描述汽车奔跑的功能
// 2.1.5 在main方法中创建一个品牌为“benz”、颜色为“black”的汽车。
String brand;//汽车品牌
String color;//颜色
double speed;//速度
public Vehicle() {
super();
}
public Vehicle(String brand, String color) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
public void setSpeed(double speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Vehicle [brand=" + brand + ", color=" + color + ", speed=" + speed + "]";
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(brand+"牌子"+color+",跑车"+",初始速度"+speed+"km/h");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle vehicle = new Vehicle("benz", "black");
System.out.println(vehicle.toString());//不写toString也行,因为会默认调用toString方法
vehicle.run();
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Car extends Vehicle {
// 2.2 定义一个Vehicle类的子类轿车类Car,要求如下:
// 2.2.1 轿车有自己的属性载人数loader(int 类型)。
// 2.2.2 提供该类初始化属性的构造方法。
// 2.2.3 重新定义run(),用打印语句描述轿车奔跑的功能。
// 2.2.4 在main方法中创建一个品牌为“Honda”、颜色为“red”,载人数为2人的轿车。
private int loader;//载人数
public Car() {
super();
}
public Car(String brand,String color,int loader) {
super(brand,color);
this.loader = loader;
}
public int getLoader() {
return loader;
}
public void setLoader(int loader) {
this.loader = loader;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Vehicle [brand=" + super.getBrand() + ", color=" + super.getColor() + ", "
+ "speed=" + super.getSpeed() + ",loader="+ loader + "]";
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(super.getBrand()+"牌子"+super.getColor()+
",跑车可能载人:"+loader+"人,"+"初始速度"+super.getSpeed()+"km/h");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle vehicle = new Car("Honda", "red", 2);
System.out.println(vehicle.toString());
vehicle.run();
}
}
- 设计三个类,分别如下:(知识点:抽象类及抽象方法)
3.1 设计Shape表示图形类,有面积属性area、周长属性per,颜色属性color,有两个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为颜色赋值的),还有3个抽象方法,分别是:getArea计算面积、getPer计算周长、showAll输出所有信息,还有一个求颜色的方法getColor。
3.2 设计 2个子类:
3.2.1 Rectangle表示矩形类,增加两个属性,Width表示长度、height表示宽度,重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,另外又增加一个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为高度、宽度、颜色赋值的)。
3.2.2 Circle表示圆类,增加1个属性,radius表示半径,重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,另外又增加两个构造方法(为半径、颜色赋值的)。
3.3 在main方法中,声明创建每个子类的对象,并调用2个子类的showAll方法。
package chapter7;
public abstract class Shape {
// 3、设计三个类,分别如下:(知识点:抽象类及抽象方法) [必做题]
// 3.1 设计Shape表示图形类,有面积属性area、周长属性per,
// 颜色属性color,有两个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为颜色赋值的),
// 还有3个抽象方法,分别是:getArea计算面积、getPer计算周长、
// showAll输出所有信息,还有一个求颜色的方法getColor。
// 3.2 设计 2个子类:
// 3.2.1 Rectangle表示矩形类,增加两个属性,Width表示长度、
// height表示宽度,重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,
// 另外又增加一个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为高度、宽度、颜色赋值的)。
double area;//面积
double per;//周长
String color;//颜色
public Shape() {
super();
}
public Shape(String color) {
super();
this.color = color;
}
public abstract double getArea();//计算面积 抽象方法必须是抽象类
public abstract double getPer();//计算周长
public abstract void showAll();//输出所有信息
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Circle extends Shape {
// 3.2.2 Circle表示圆类,增加1个属性,radius表示半径,
// 重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,另外又增加
// 两个构造方法(为半径、颜色赋值的)。
// 3.3 在main方法中,声明创建每个子类的对象,
// 并调用2个子类的showAll方法。
double radius;//半径
public Circle() {
super();
}
public Circle(double radius,String color) {
super(color);
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
// return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override
public double getPer() {
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
@Override
public void showAll() {
System.out.println("该圆类的半径为:" + radius +
"面积为:" + getArea() + "周长为:" +
getPer() + "颜色为:" + super.getColor());
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
// 3.2 设计 2个子类:
// 3.2.1 Rectangle表示矩形类,增加两个属性,Width表示长度、
// height表示宽度,重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,
// 另外又增加一个构造方法(一个是默认的、一个是为高度、宽度、颜色赋值的)。
// 3.2.2 Circle表示圆类,增加1个属性,radius表示半径,
// 重写getPer、getArea和showAll三个方法,另外又增加两个构造方法(为半径、颜色赋值的)。
// 3.3 在main方法中,声明创建每个子类的对象,并调用2个子类的showAll方法。
double width;//长度
double height;//宽度
public Rectangle() {
super();
}
public Rectangle(double width, double height,String color) {
super(color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return width * height;
}
@Override
public double getPer() {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
@Override
public void showAll() {
System.out.println("该矩形的长为:" +width+"宽为 :" +height +
"面积为:" + getArea() + "周长为:" + getPer()+"颜色为:"+super.getColor());
}
}
package chapter7;
public class TestShape {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(10,20,"black");
rect.showAll();
Circle circle = new Circle(10,"red");
circle.showAll();
}
}
- Cola公司的雇员分为以下若干类:(知识点:多态)
4.1 ColaEmployee :这是所有员工总的父类,属性:员工的姓名,员工的生日月份。方法:getSalary(int month) 根据参数月份来确定工资,如果该月员工过生日,则公司会额外奖励100 元。
4.2 SalariedEmployee : ColaEmployee 的子类,拿固定工资的员工。属性:月薪
4.3 HourlyEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,按小时拿工资的员工,每月工作超出160 小时的部分按照1.5 倍工资发放。属性:每小时的工资、每月工作的小时数
4.4 SalesEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,销售人员,工资由月销售额和提成率决定。属性:月销售额、提成率
4.5 定义一个类Company,在该类中写一个方法,调用该方法可以打印出某月某个员工的工资数额,写一个测试类TestCompany,在main方法,把若干各种类型的员工放在一个ColaEmployee 数组里,并单元出数组中每个员工当月的工资。
package chapter7;
public class ColaEmployee {
// 4.1 ColaEmployee :这是所有员工总的父类,
// 属性:员工的姓名,员工的生日月份。
// 方法:getSalary(int month) 根据参数月份来确定工资,
// 如果该月员工过生日,则公司会额外奖励100 元。
String name;//员工姓名
int month;//员工生日
public ColaEmployee(String name, int month) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.month = month;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
return 0;
}
}
package chapter7;
public class SalariedEmployee extends ColaEmployee {
// 4.2 SalariedEmployee : ColaEmployee 的子类,
//拿固定工资的员工。属性:月薪
double monSalary;//月薪
public SalariedEmployee(String name,int month,double monsalary) {
super(name,month);
this.monSalary = monsalary;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
if(super.month == month) {//过生日
return monSalary + 100;
}else {
return monSalary;
}
}
}
package chapter7;
public class HourlyEmployee extends ColaEmployee {
// 4.3 HourlyEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,
// 按小时拿工资的员工,每月工作超出160 小时的部分按照
// 1.5 倍工资发放。属性:每小时的工资、每月工作的小时数
private int hourSalary;//时薪
private int hourNum;//每月工作的小时数
public HourlyEmployee(String name, int month,int hourSalary,int hourNum) {
super(name, month);
this.hourSalary = hourSalary;
this.hourNum = hourNum;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
if(super.month == month) {
if(hourNum > 160) {
return hourSalary * 160 +
hourSalary * (hourNum - 160) * 1.5
+ 100;
}else {
return hourSalary * hourNum + 100;
}
}else {
if(hourNum > 160) {
return hourSalary * 160 +
hourSalary * (hourNum - 160) * 1.5;
}else {
return hourSalary * hourNum;
}
}
}
}
package chapter7;
public class SalesEmployee extends ColaEmployee {
// 4.4 SalesEmployee :ColaEmployee 的子类,
// 销售人员,工资由月销售额和提成率决定。
// 属性:月销售额、提成率
private int monthSales;//月销售额
private double royaltyRate;//提成率
public SalesEmployee(String name, int month,int monthSales,double royaltyRate) {
super(name, month);
this.monthSales = monthSales;
this.royaltyRate = royaltyRate;
}
public double getSalary(int month) {
if(super.month == month) {
return monthSales * royaltyRate + 100;
}else {
return monthSales * royaltyRate;
}
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Company {
// 4.5 定义一个类Company,在该类中写一个方法,
// 调用该方法可以打印出某月某个员工的工资数额,
// 写一个测试类TestCompany,在main方法,
// 把若干各种类型的员工放在一个ColaEmployee 数组里,
// 并打印出数组中每个员工当月的工资。
public void getSalary(ColaEmployee c,int month) {
System.out.println(c.name + " 在 " + month + " 的月薪为 " + c.getSalary(month));
}
}
package chapter7;
public class TestCompany {
// 4.5 定义一个类Company,在该类中写一个方法,
// 调用该方法可以打印出某月某个员工的工资数额,
// 写一个测试类TestCompany,在main方法,
// 把若干各种类型的员工放在一个ColaEmployee 数组里,
// 并打印出数组中每个员工当月的工资。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColaEmployee[] cel = {
new SalariedEmployee("salariedEmployee", 6, 30000),
new HourlyEmployee("hourlyEmployee", 5, 100, 300),
new SalesEmployee("salesEmployee", 3, 7000000, 0.3)
};
for (int i = 0; i < cel.length; i++) {
new Company().getSalary(cel[i],7);
}
}
}
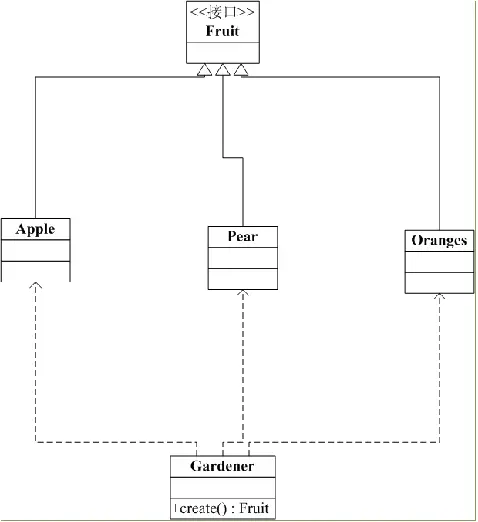
- 利用接口实现动态的创建对象
5.1 创建4个类:苹果 香蕉 葡萄 园丁
5.2 在三种水果的构造方法中打印一句话. 以苹果类为例
class apple
{
public apple()
{
System.out.println(“创建了一个苹果类的对象”);
}
}
类图如下:
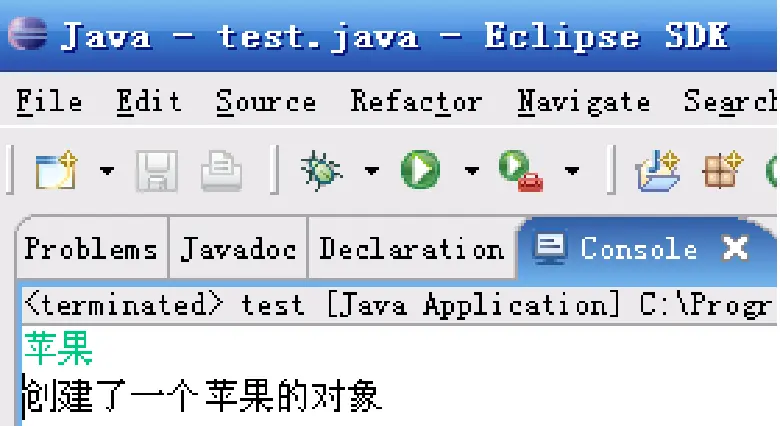
5.3 要求从控制台输入一个字符串,根据字符串的值来判断创建三种水果中哪个类的对象
如图:
package chapter7;
public interface Fruit {
}
package chapter7;
public class Apple implements Fruit {
public Apple() {
System.out.println("创建了一个Apple类的对象");
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Pear implements Fruit{
public Pear() {
System.out.println("创建了一个Pear类的对象");
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Oranges implements Fruit{
public Oranges() {
System.out.println("创建了一个Oranges类的对象");
}
}
package chapter7;
public class Gardener {
public Fruit create(String fruitName) {
Fruit f = null;
switch (fruitName) {
case "apple":
f = new Apple();
break;
case "pear":
f = new Pear();
case "oranges":
f = new Oranges();
default:
System.out.println(fruitName);
break;
}
return f;
}
}
package chapter7;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestGardener {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入水果的英文名称");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String fruitName = scanner.nextLine();
new Gardener().create(fruitName);
}
}
- 编写三个系别的学生类:英语系,计算机系,文学系(要求通过继承学生类)
6.1各系有以下成绩: 英语系: 演讲,期末考试,期中考试; 计算机系:操作能力,英语写作,期中考试,期末考试; 文学系: 演讲,作品,期末考试,期中考试;
6.2各系总分评测标准: 英语系: 演讲 50% 期末考试 25% 期中考试 25% 计算机系: 操作能力 40% 英语写作 20% 期末考试 20% 期中考试 20% 文学系: 演讲 35% 作品 35% 期末考试 15% 期中考试 15%
6.3定义一个可容纳5个学生的学生类数组,使用随机数给该数组装入各系学生的对象,然后按如下格式输出数组中的信息: 学号:XXXXXXXX 姓名:XXX 性别:X 年龄:XX 综合成绩:XX
package chapter7;
public class Student {
int stuNo;//学生学号
String stuName;//学生姓名
char stuSex;//学生性别
int stuAge;//学生年龄
double stuScore;//学生成绩
public Student(int stuNo, String stuName, char stuSex, int stuAge, double stuScore) {
super();
this.stuNo = stuNo;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.stuSex = stuSex;
this.stuAge = stuAge;
this.stuScore = stuScore;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [stuNo=" + stuNo + ", stuName=" + stuName + ", stuSex=" + stuSex + ", stuAge=" + stuAge
+ ", stuScore=" + stuScore + "]";
}
}
package chapter7;
public class EnglishStu extends Student {
double speechScore;//演讲分数
double finalScore;//期末考试分数
double midtermScore;//其中考试分数
public EnglishStu(int stuNo, String stuName, char stuSex, int stuAge,
double speechScore,double finalScore,double midtermScore) {
super(stuNo, stuName, stuSex, stuAge, speechScore * 0.5 + finalScore * 0.25 + midtermScore * 0.25);
this.speechScore = speechScore;
this.finalScore = finalScore;
this.midtermScore = midtermScore;
}
}
package chapter7;
public class ComputerStu extends Student {
double operScore;//操作能力分数
double englishScore;//英语写作分数
double finalScore;//期末分数
double midtermScore;//其中考试
public ComputerStu(int stuNo, String stuName, char stuSex, int stuAge,
double operScore,double englishScore,double finalScore,double midtermScore) {
super(stuNo, stuName, stuSex, stuAge, operScore * 0.4 + englishScore * 0.2 +
finalScore * 0.2 + midtermScore * 0.2);
this.operScore = operScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.finalScore = finalScore;
this.midtermScore = midtermScore;
}
}
package chapter7;
public class LiteratureStu extends Student {
double speechScore;//演讲分数
double worksScore;//作品分数
double finalScore;//期末考试分数
double midtermScore;//其中考试分数
public LiteratureStu(int stuNo, String stuName, char stuSex, int stuAge,
double speechScore,double worksScore,double finalScore,double midtermScore) {
super(stuNo, stuName, stuSex, stuAge,
speechScore * 0.35 + worksScore * 0.35 +
finalScore * 0.15 + midtermScore * 0.15);
this.speechScore = speechScore;
this.worksScore = worksScore;
this.finalScore = finalScore;
this.midtermScore = midtermScore;
}
}
package chapter7;
public class TestStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 6.3定义一个可容纳5个学生的学生类数组,
// 使用随机数给该数组装入各系学生的对象,
// 然后按如下格式输出数组中的信息:
// 学号:XXXXXXXX 姓名:XXX 性别:X 年龄:XX 综合成绩:XX
Student[] stu_prototype = {
new EnglishStu(10, "english" + Math.round(10 * Math.random()), '0', 20,
Math.round(100 * Math.random()), Math.floor(100 * Math.random()),
Math.round(100 * Math.random())),
new ComputerStu(11, "computer" + Math.round(10 * Math.random()), '1',20,
Math.round(100 * Math.random()), Math.round(100 * Math.random()),
Math.round(100 * Math.random()), Math.round(100 * Math.random())),
new LiteratureStu(12, "liter" + Math.round(10 * Math.random()), '0', 20,
Math.round(100 * Math.random()), Math.round(100 * Math.random()),
Math.round(100 * Math.random()), Math.round(100 * Math.random()))
};
Student[] stu = new Student[5];
for (int i = 0; i < stu.length; i++) {
stu[i] = stu_prototype[(int) Math.round(Math.random() * stu_prototype.length)];
}
for (int j = 0; j < stu.length; j++) {
System.out.println(stu[j].toString());
}
// Student [stuNo=10, stuName=english2, stuSex=0, stuAge=20, stuScore=71.5]
// Student [stuNo=11, stuName=computer5, stuSex=1, stuAge=20, stuScore=59.6]
// Student [stuNo=10, stuName=english2, stuSex=0, stuAge=20, stuScore=71.5]
// Student [stuNo=10, stuName=english2, stuSex=0, stuAge=20, stuScore=71.5]
// Student [stuNo=12, stuName=liter8, stuSex=0, stuAge=20, stuScore=49.15]
}
}
分割线
相关信息
以上就是我关于 Java初级测试题七-面向对象高级特性(6-6) 知识点的整理与总结的全部内容,希望对你有帮助。。。。。。。